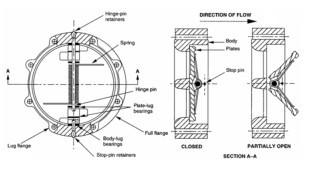
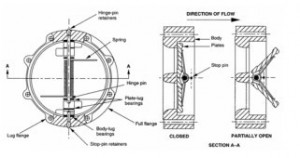
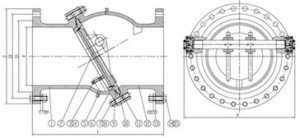
The tilting-disc swing check valve is another variant of the basic type of check valve. In these valves, the disc swings partly through the seat. The geometry for sealing and avoiding jamming is more complicated than for other swing checks. One variety pivots the disc in the seat area – but somewhat off-center. This means that the zones around the pivot are more difficult to seal, analogous to the problem of the symmetrical butterfly valve. The disc is nearly balanced, reducing slamming. Seal material is basically Buna-N, but Viton, Teflon, and even monel are possible. The valve is a very short wafter type, so the open disc protrudes beyond the body.
Tilting-disc valves with the pivot outside the seating area are available in many forms. The geometry of the pivot location and angle of the seating surfaces allows the disc to lift away from the seat at all points and prevents the disc from becoming wedged so tightly in the seat that it cannot move. Extreme and sudden temperature changes and differentials get close consideration in this. The disc and seat may be likened to a slice from a bottle stopper, made at an oblique angle to the cone axis to allow the “stopper” to be removed by a twist about the pivot downstream. The machining of the oval seat ring and disc in this valve requires skill. In some instances, the cone is cut at right angles, but location of the pivot downstream and above the valve axis permits the top of the disc to swing through the seat.
In some tilting-disc check valves, the disc has a slight clearance on the pivot, to help assure a tight seat. In other tilting-disc vales, the heavy pivot shaft is rigidly attached to the disc and supported in close-clearance bearings. The pivot shaft is generally large-diameter in tilting-disc valves, so attachment of dashpots, indicators, and limit switches is easy.
Because of the partial balance of the disc, the fluid-dynamic characteristics of the disc are important. The forward-flowing fluid must open the disc easily, and then hold it open with little flutter. When flow slows and stops, the disc must close quickly and silently. Several tilting discs have curved undersurfaces to develop fluid-dynamic forces. One variety has a flap above the main disc, which also serves to limit disc opening, removing a load from the main disc.
Access to the internals of some tilting-disc check valves, when they are mounted in the line, is through conventional bonnets or removable plates. The internals of other models are inaccessible, because the valve body is of the wafer or short-spool type. In general, valves that must be welded into the line tend to resemble the standard types of checks, with welds at a safe distance from the seat. One line of tilting-disc checks has obliquely split bodies for pressure classes to 1500 ANSI, but is a wafer body between weld-end flanges in higher-pressure classes.
SGV Tilting Disc Check Valves consist of a cylindrical housing, with a pivoted circular disc. The pivots are located just above the center of the disc, and offset from the plane of the body seat. This design gives a bell-crank action to the disc. The seat is of circular bevel type and the disc drops in or out of contact without rubbing or sliding.It is mounted at the outlet pipeline of the pressurized output water pump in industrial (and urban) water supply and drainage system,high-rises, sewage discharge, hotel and restaurants, functioned to cut off the backflow of medium and eliminate destructive water hammer.
Featured by small volume, lightweight, Low head loss ,easy installation, Energy efficient, little occupation of space, saver if time and labor for servicing and maintenance, and etc., this valve is an optimal solution for water supply and drainage products
API 600 Bolted Bonnet Steel Gate Valves for Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries,ISO10434,BS1414 Gate valve
API 600 Bolted Bonnet Steel Gate Valves for Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries
API Standard 600, Eleventh Edition , October 2001
ISO 10434 Gate Valves: 1998 ( BS1414 Gate Valves)
ANSI/API Std 600-2001
Contents Included
Introduction, Scope, Normative references, Definitions, Pressure/temperature ratings, Design, Body wall thickness,Bonnet wall thickness , Body dimensions, Flanged, Butt-welding ends, Body seats, Openings, Bonnet dimensions, Bonnet-to-body joint, Gate, Yoke, Stem and stem nut, Packing and packing box, Bolting, Operation, Auxiliary connections, Materials, Materials other than trim materials, Trim, Repair, Testing, inspection and examination, Pressure tests, Shell test, Closure tightness test , Backseat test, Optional closure tightness test, Inspection, At the valve manufacturer’s factory, Other than at the valve manufacturer’s factory, Extent of inspection, Examination, Supplementary examination, Marking, Legibility, Body markings, Ring joint markings, Identification plate marking, Preparation for despatch
Bolted bonnet steel gate valves for petroleum and natural gas industries
1 Scope
This International Standard specifies the requirements for a heavy duty series of bolted bonnet steel gate valves for petroleum refinery and related applications where corrosion, erosion and other service conditions indicate a need for full port openings, heavy wall sections and extra large stem diameters.
This specification sets forth the requirements for the following gate valve features:
— bolted bonnet;
— outside screw and yoke;
— rising stems;
— non-rising handwheels;
— single or double gate;
— wedge or parallel seating;
— metallic seating surfaces;
— flanged or butt-welding ends.
It covers valves of the nominal sizes DN:
25; 32; 40; 50; 65; 80; 100; 150; 200; 250; 300; 350; 400; 450; 500; 600
and is applicable for pressure designations PN:
20; 50; 110; 150; 260; 420
when metric sized bolt holes are provided in end flanges and PN designations are marked on the valve body.
It also covers valves of the corresponding nominal pipe sizes NPS:
1; 11/4; 11/2; 2; 21/2; 3; 4; 6; 8; 10; 12; 14; 16; 18; 20; 24
and applies for equivalent nominal Class ratings:
150; 300; 600; 900; 1500; 2500
when inch-sized bolt holes are provided in end flanges and Class designations are marked on the valve body.It also covers additional marking requirements for valves that are PN (or Class) designated but have flanges drilled for inch (or metric) bolt holes.
2 Normative references
The following standards contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this International
Standard. At the time of the publication, the editions indicated were valid. All standards are subject to revision, and parties to agreements based on this International Standard are encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying the most recent editions of the standards indicated below. Members of IEC and ISO maintain registers of currently valid International Standards.
ISO 7-1:1994,Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads—Part 1: Dimensions, tolerances and designation.
ISO 4200:1991,Plain end steel tubes, welded and seamless—Dimensions. ISO 5208:1993,Industrial valves—Pressure testing of valves. ISO 5209:1977,General purpose industrial valves—Marking.
ISO 5210:1991,Industrial valves—Multi-turn valve actuator attachments.
ISO 5752:—1),Metal valves for use in flanged pipe systems—Face-to-face and centre-to-face dimensions.
ISO 6708:1995,Pipework components — Definition and selection of DN (nominal size).
ISO 7005-1:1992,Metallic flanges — Part 1: Steel flanges.
ISO 7268:1983,Pipe components — Definition of nominal pressure.
ASME B1.1:1989,Unified inch screw threads (UN and UNR thread form).
ASME B1.5:1988 (R1994),Acme screw threads.
ASME B1.8:1988 (R1994),Stub Acme screw threads.
ASME B1.12:1987 (R1992),Screw threads — Class 5 interference — Fit thread.
ASME B1.20.1:1983 (R1992),Pipe threads, general purpose (inch).
ASME B16.5:1996,Pipe flanges and flanged fittings.
ASME B16.34:1996,Valves — Flanged, threaded and welding end.
ASME B18.2.2:1987 (R1993),Square and hex nuts (inch series).
ASTM A193:1996,Specification for alloy steel and stainless steel bolting materials for high-temperature service.
ASTM A194:1996,Specification for carbon and alloy steel nuts for bolts for high-pressure and high-temperature service.
ASTM A307:1994,Specification for carbon steel bolts and studs, 60 000 psi tensile strength.
MSS SP-55:1985 (R1990),Quality standard for steel castings, visual surface examination.
API Standard 600/ISO 10434:1998 American Petroleum Institute———————————
If you have any quesiton or enquiry about API600 gate valves, feel free contact Sangong team with info@sangongvalve.com. SGV also offer special API603 cast stainless steel gate valve.
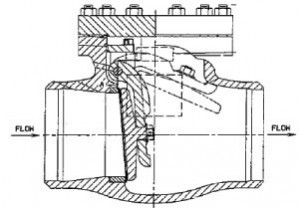
Válvula de balanço, API dupla flange Válvula de balanço, API flanged swing check valve
Nome do produto: Válvula de balanço (swing type check valve)
É geralmente apareceu com dupla flange da válvula de verificação do balanço, uma válvula de retenção tradicional, tem aplicação extremamente ampla. É simples e confiável, o que significa que a tecnologia é bastante maduro e estável, fácil de reparar. API válvula de swing e balanço DIN válvula adotar disco diferente pendurado estrutura.
Standard e escopo:
Tamanho: NPS 2 “~ 36” DN50 ~ DN900 Avaliação da pressão: Classe 150 ~ 2500 PN2.5 ~ PN100 Conexão: face aumentado, Soldar, face Anel conjunta, face Masculino, Feminino rosto, solda de soquete e assim por diante Material: aço carbono, aço inoxidável, liga e assim por diante Projeto e Fabricação: ASME B16.34 e API 6D, BS EN 1868, DIN 3840 Inspeção e teste: API 598 ou API 6D, BS EN12569 Dimensão final flange: ASME B16.5 (NPS para ≤ 24); ASME B 16,47 série B (o nosso padrão normal), API 605 ou ASME B16.47 série A, MSS SP-44 (para NPS> 24; BS EN 1092 – 1 BW dimensão final: ASME B16.25 Soldadas-dimensão: ASME B16.11 De ponta a ponta: ASME B16.10, BS EN 558-1, DIN 3202, ISO 5752 TEMPERATURA E PRESSÃO: ASME B16.34 Dimensão da parede espessura: API 600 e BS 1868, API603 Característica de projeto Assento Para o carbono válvula de retenção de aço swing, o assento é normalmente de aço forjado. A superfície de vedação da sede de pulverização é soldada com liga dura exigidas pelo cliente. Sede roscada renovável é usado para NPS ≤ 8 válvulas, e soldados no assento também pode ser opcional se a ser solicitado pelo cliente. Soldado no assento é usado para NPS ≥ 10 carbono válvulas de aço.Para Válvula de aço inoxidável de verificação, assento integral é usualmente adotados, ou para soldar liga dura diretamente integralmente. Rosqueado ou soldada no lugar também é opcional para válvula de aço inoxidável de verificação, se necessário.
Corpo-a-Bonnet Conjunto: Junta
Aço inoxidável + de grafite flexível feridos é usado para Class150 e Class300 válvula de retenção; aço inoxidável + de grafite flexível feridos é usado para Class600 válvula de retenção, e junta conjunta também é opcional para Class600 válvula de retenção; junta anel comum é usado para Class900 válvula de retenção , projeto do selo de pressão é usado para Class1500 ~ Class2500 válvulas de retenção.
Conexão corpo e capota
O corpo ea capota de Class150 ~ Class900 válvulas de retenção são normalmente conectados com pregos e porcas. E o corpo e tampa de Class1500 ~ Class2500 válvulas de retenção são geralmente do projeto Selo de pressão.
Dual plate check valve – wafer or lug or flange type dual plate check valve
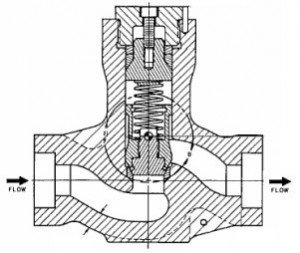
Check valves are automatic in operation and designed to prevent reversal of flow in fluid piping systems. So when the medium is back-going, valve disc will automatically close to avoid accidents. The check valves are maintained open by the flow of fluid in the forward direction and are closed by a spring force, or by the weight of the closing mechanism, or by back pressure of the fluid.
Dual plate check valve , one type check valve, typicaly see with wafer dual plate check valve, lug type dual plate check valve, flanged dual plate check valve, as per connection type, butt weld is very rare. It is also called split disc check valve, butterfly check valve(like a butterfly valve, this type valve has more similar structure with butterfly valve, compare with gate, globe, ball valve), duo disc spring loaded check valve(double disc with spring).
SGV offer dual plate check valve with stainless steel trim, usually CF8, CF8M, CF3,CF3M,(304, 316,304L,316L) Duplex steel, carbon steel disc is available but not suggested, Enconel spring, metal seating, is our noraml combination( with stem, spring, washer, gasket, hex nut and other necessary fittings).
It is designed to overcome the size and pressure drop limitations of the swing and disc type wafer check valves (somebody think dual plate is also swing type check valve ). It has many available types or modes so as to meet the generally complex and specific requirements, both in the industrial process and the daily life.
The disc(two plates) of dual plate check valves are held against the seat by a torsion spring mounted on the hinge. And the external mounted retainer pins of valve are needed to hold the hinge in the centre of the flow path. Besides, an improved design secures the hinge internally and the valve mechanism is entirely sealed within the body so to prevent out leakages caused by retainer pin effectively.
Usually Applied Standard:
Design and manufacture: API594, API6D, JB/T8937.
Pressure-Temperature grade: ANSIB16,34, DIN2401, GB/T9124, HG20604, HG20605, SH3406, JB/T74, ANSI B16.34 Length of structure (face to face,end to end): API594, API6D, DIN3202, JB/T8937 Inspection and test : API598, JB/T9092 Pipe flange:APIT605,ASMEB16.47,ANSIB16.5,DIN2543~2548,JB/T74~90,GB/T9112/9124, HG20592~20635, SH3406, GB/T13042,
Application of Plastic Valve in Industrial Piping
Application of Plastic Valve in Industrial Piping and Requirements
The advantages of using plastics are constantly being discovered. Over the past few years, there has been a dramatic increase in the application of plastic valves and piping systems in areas where metal valves were thought to be the only solution. So plastic or metal? It should consider valve base seal test, valve seal test, valve strength test, long term valve test, fatigue test and operating torque test by using reasoble method and standard, to compare cost performance of plastic valve and metal valve.
There are many types of plastic valves.Include Ball valves,Butterfly valves,Needle valves,Drain valves, Float valves, Gate valves, Globe va lves, knife valves (similar structure with gate), pinch valves, Check valves, Poppet valves, Plug or stop-cock valves, Diaphragm valves, Directional valves , Diverter valves. Other types of plastic valves include shut off valves, solenoid valves, sanitar valves or hygienic valves, sampling or dispensing valves, and toggle valves.
Selecting plastic valves requires an analysis of performance specifications, actuation methods, and connection types.
Performance specifications include valve size, pressure rating, number of ports or ways, media temperature, and valve flow coefficient. Suppliers specify valves according to metric or English (imperial) measurements.
Some plastic valves are actuated manually, by a hand wheel or crank, or with mechanical devices such floats and cams. Others are actuated by electric, pneumatic, electro-hydraulic, or electro-hydraulic methods.
Connection types for plastic valves can be many. Examples include compression fittings, bolt flanges, clamp flanges, union connections, tube fittings, butt welds, and socket welds. Plastic valves with internal or external threads for inlet or outlet connections are also available.
Nowadays Plastic valves are been used for following application:powders, rendering wastes, sludge, slurry, ash slurry, coolants, hazardous materials, liquid metal,wastewater, gasoline, diesel fuel, lubricants, air and compressed air, hot and cold water, salt water,high viscosity fluids, hydraulic fluid liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), natural gas, abrasive materials, acids, and adhesives.
Valve Delevepoment Trend:Versatile Hydraulic control valve, Intelligent electric control valve, energy-saving valve
Valve Delevepoment Trend: Versatile Hydraulic control valve(high performance, butterfly valve), Intelligent electric control valve(remote control, gate valve), energy-saving valve(standardardization, seris valve)
With the development of science and technology, the competition for valves is more and more fierce and at the same time the future development of the valve has been the hot focus in the market. Hydraulic control valve, electric control valve, energy-saving valve are the three main valves in the market, what will be their development in the future.
1. Hydraulic control valve(like the butterfly valve)– whose development trend is versatile. To be high performance is necessary for this kind of valve, like large emission, resistance to corrosion, high sensitivity, abrasion, leakiness and so on. Besides for the high performance, the valve is also required to adopt the integrated technology, computer technology and monitoring technology. In a word, the product with the features of reliability, safety and comfort is the aim for the manufactories.
2. Intelligent electric control valve (like the motor operated gate valve) should aim at having the function of remote control. Nowadays although the control valve is widely used in all kinds of industries, it still can not keep up with the development of industries and can not meet the need for different environment. The great projects need the large-sized control valve with high performance. To develop small-sized ones can satisfy the requirements of narrow jobs such as digging the canal, burying cable. What’s more, in order to monitor, control and improve the working condition for operators, it is a trend to develop intelligent electric valve operated through remote control. If the company can first develop this product, it is very potential for him to control the market.
3. The energy-saving valve used for engineer projects should be manufactured in series. In order to satisfy the need of the market, it is urgent to develop series of the valves including large-sized one, small-sized one or new type one. Besides, it is necessary to develop the variable-speed valves, such as swamp type, desert type, the type for high temperature and high pressure, heavy or light type and so on. All in all, if the company wants to conquer the market share, it is a better way to develop high effective energy-saving valve with multi-function. Among so many energy-saving valves, the relatively promising products are large-sized ones, caterpillar gate valves with large power and small-sized butterfly valves.
Besides the above, it is important for a company to make the valves to follow the trend of seriation, universalization and standardization. Meanwhile, high level, good safety and excellent performance advanced valves are needed in the market.
Check valve-Non-return valves:lift check valve,swing check valve,butterfly check valve,dual plate check vavle,tilting disc check valve
Check Valve
Check valves or Non-return valves (NRV) are normally installed in piping to avoid back flow. Rotating equipment such as pump, compressor, etc will always be equipped with NRV(s) on the discharge to avoid back flow when rotating equipment is shut. Back flow creates severe surging to the rotating equipment and potentially damage the equipment. In certain process system, NRV will be employed to avoid contamination, overheating, etc due to back flow.
Check valves or Non-return valves (NRV) -One way valve is basically an automatic valve open to allow forward flow and close to against reverse flow. In principle, it split into four basic types. There are swing, dual-plate, tilting disc and lifting type. Wrong selection of check valve type can leads to operability problem, leakage and continual maintenance issue.
– higher pressure drop is expected.
– equipped with small return spring to facilitate valve closure on reverse flow
– two type of seat. hard seat for for high differential pressure sealing and resilient seat for low differential pressure sealing
– shortest travel length. Fastest response.
– excellent performance for low and/or pulsating flows
– not good for fluid with particles
– Body install horizontal with disc / piston vertically
– Small check valve range from 1/2″ to 2″ lift piston type check valve
– Prefer operate in full open position
Minimum Recommended Line Velocity, Vmin (ft/s) = 12 SQRT (v)
where
v = Specific Volume of the Fluid (ft3/lb)
– Tight sealing / shut-off
– Low pressure drop
– Susceptible to water hammer
– Not good for low flow and/or pulsating flow
– Vertical (upward flow) & horizontal installation
– Easiest check valve to maintain
– Prefer operate in full open position
Swing check valves should be sized such that the flow velocity in the line is sufficient to hold the disc in the fully open position.
Minimum Recommended Line Velocity, Vmin (ft/s) = 75 SQRT(v)
where
v = Specific Volume of the Fluid (ft3/lb)
The characteristic of dual plate check valve is pretty same as swing check valve.
– low pressure drop
– Not good for low flow and/or pulsating flow
– Vertical (upward flow) & horizontal installation
– Faster opening and closure compare to swing check valve
– Susceptible to water hammer (lesser than Swing check valve)
– Prefer operate in full open position
– Fast opening and closing without damage to disc and seat
– Stable at low and pulsating flows
– Moderate pressure drop. Lower than lifting check valve but higher than swing check valve
– Vertical (upward) & horizontal installation
– Moderate tight sealing
– Prefer operate in full open position
Minimum Recommended Line Velocity, Vmin (ft/s) = 24 sqrt (v)
where
v = Specific Volume of the Fluid (ft3/lb)
Selection Consideration
There are four (4) main criteria shall be considered for the selection of check valve type :
non-slam characteristic
pressure loss
cost
application
Comparative rating for each type of check valve have been provided for these criteria (specifically first two technical criteria). These rating will be plotted on a Check Valve Comparative Selection Chart and together budget for final selection.
Friend Link of Sangong
Friend Link of Sangong:
API ANSI VALVE RELATED SPECIFICATIONS, CODES AND STANDARDS
API ANSI VALVE RELATED SPECIFICATIONS, CODES AND STANDARDS
The following list of codes and standards are usually referenced within this Specification, refer to “Project Codes and Standards” for the complete project list, as minimum.
API 594
Check Valves: Wafer, Wafer-Lug, and Double Flanged Type
API 598
Valve Inspection and Testing
API 5L
Line Pipe Specification
API 600
Bolted Bonnet Steel Gate Valves for Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries
API 602
Compact Steel Gate Valves – Flanged, Threaded and Weld End
API 603
Corrosion Resistant, Bolted Bonnet Gate Valves – Flanged and Buttweld
Continue reading “API ANSI VALVE RELATED SPECIFICATIONS, CODES AND STANDARDS”
Valve Testing, Marking, Shippment Preparation, Dimension, Inspection, Substitution&Variation, Guarantee, Cercification&Tracebility, Documentation Requirement -Project SGPK03
12. TESTING
1 Floating ball, gate, globe, needle and piston check valves, shall be pressure tested in accordance with BS6755 Part 1, leakage rate ‘A’ (i.e. zero) unless specified
otherwise in the data sheet.
2 Trunnion mounted ball, butterfly, swing check and dual plate wafer check valves,
shall be pressure tested in accordance with API 598. Butterfly valves 14”NPS and
larger shall also be subjected to a disk strength test in accordance with BS5155.
3 Where stated on the valve data sheet, fire type-testing shall be in accordance with BS6755 Part 2, API 6FA or API 607 as applicable. All valves offered shall be
qualified by applicable fire test certification, details of which shall be available for Purchaser review, if requested.